|
Case Report
Ultrasound-guided bichectomy: A case report of a novel approach
1 Department of Dental Clinics, Oral Pathology, and Oral Surgery, School of Dentistry, Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil
2 Doctor of Dental Surgery, Belo Horizonte, Brazil
3 Department of Morphology, Biological Sciences Institute, Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil
4 Doctor of Dental Surgery, Radiologist of the Hermes Pardini Group, Belo Horizonte, Brazil
Address correspondence to:
Alexandre Godinho Pereira
Department of Dental Clinics, Oral Pathology, and Oral Surgery, School of Dentistry, Federal University of Minas Gerais, Rua Prof. Moacir Gomes de Freitas, 688 - 31.270-901, Belo Horizonte, MG,
Brazil
Message to Corresponding Author
Article ID: 101086Z01AP2020
Access full text article on other devices

Access PDF of article on other devices

How to cite this article
Pereira AG, Napoli GF, Gomes TB, Rocha LPC, Rocha TDC, e Silva MRMA. Ultrasound-guided bichectomy: A case report of a novel approach. Int J Case Rep Images 2020;11:101086Z01AP2020.ABSTRACT
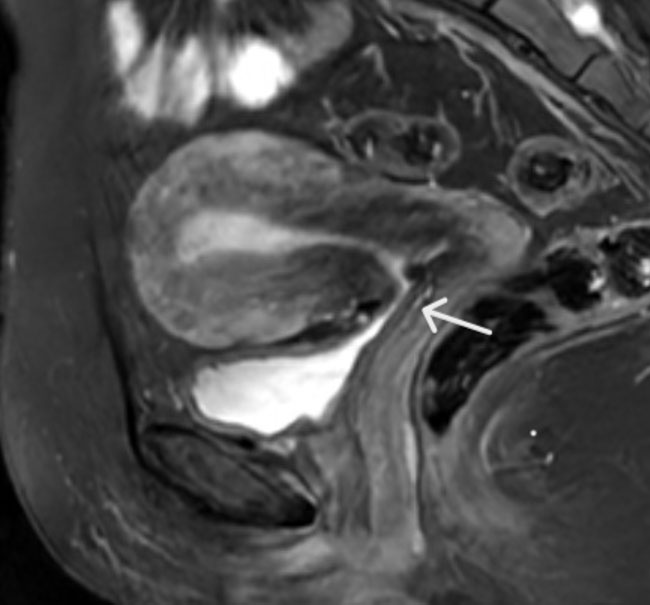
Introduction: Bichectomy promotes reduction of cheek volume by partial removal of the buccal fat pad. Like any other surgical procedure, there are inherent risks that can lead to severe complications. To minimize those risks, a novel approach using real-time ultrasonography (US) imaging during the procedure was performed on a difficult bichectomy case with anatomical variation in the buccal fat pad position.
Case Report: A 25-year-old female patient was referred for bichectomy on her left cheek. An ultrasound scan was performed and an anatomical variation in position was detected. The patient’s left buccal fat pad was located deep in the masseteric area and in close relationship with branches from the facial vein and the transverse facial artery. Since there was an increased risk to perform the surgery, a guided bichectomy was performed using real time ultrasound imaging to guide the initial incision, location, and excision. The procedure was performed without any complication and the clinical success was assessed by ultrasonography in the postoperative period.
Conclusion: The US performed during the surgery made it possible to safely access and remove the buccal extension with minimal risk for the patient. The ultrasound proved to be useful to demonstrate the relationship among the buccal fat pad and adjacent structures and to detect anatomical variation in its position, allowing a safer surgical procedure to be performed
Keywords: Adipose tissue, Case report, Face, Lipectomy, Ultrasonography
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
Author Contributions
Alexandre Godinho Pereira - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Drafting the article, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Gregory Fernandes Napoli - Acquisition of data, Drafting the article, Final approval of the version to be published
Thiago Bissoli Gomes - Acquisition of data, Drafting the article, Final approval of the version to be published
Luiz Paulo Carvalho Rocha - Interpretation of data, Drafting the article, Final approval of the version to be published
Tânia de Carvalho Rocha - Acquisition of data, Interpretation of data, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Micena Roberta Miran Alves e Silva - Substantial contributions to conception and design, Revising it critically for important intellectual content, Final approval of the version to be published
Guarantor of SubmissionThe corresponding author is the guarantor of submission.
Source of SupportNone
Consent StatementWritten informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this article.
Data AvailabilityAll relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Conflict of InterestAuthors declare no conflict of interest.
Copyright© 2020 Alexandre Godinho Pereira et al. This article is distributed under the terms of Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium provided the original author(s) and original publisher are properly credited. Please see the copyright policy on the journal website for more information.