|

|
 |
|
Case Report
| ||||||
| Self resolving non-parasitic splenic cyst: A case report | ||||||
| Meetal Shah1, Abdul Quyyum Khan2, Maria Vittoria Cavalletti3, Luciano Perrone4, Chenji Ratnavel5, Giovanni Domenico Tebala6 | ||||||
|
1MBCHB, Foundation Doctor 1, General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Unit, Surgical Department, Noble's Hospital, Douglas, Isle of Man.
2MBBS MSC(Edin), Specialty Doctor, General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Unit, Surgical Department, Noble's Hospital, Douglas, Isle of Man. 3MD, Consultant Anaesthetist, Department of Anaesthesia, Aurelia Hospital, Rome, Italy. 4MD, Surgical Resident, General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Unit, Surgical Department, Noble's Hospital, Douglas, Isle of Man. 5MD, FRCS FRCPS, (Glasg), Associate Specialist, General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Unit, Surgical Department, Noble's Hospital, Douglas, Isle of Man. 6MD FRCS, Consultant Surgeon, General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Unit, Surgical Department, Noble's Hospital, Douglas, Isle of Man. | ||||||
| ||||||
|
[HTML Abstract]
[PDF Full Text]
[Print This Article]
[Similar article in Pumed] [Similar article in Google Scholar] 
|
| How to cite this article |
| Shah M, Khan AQ, Cavalletti MV, Perrone L, Ratnavel C, Tebala GD. Self resolving non-parasitic splenic cyst: A case report. International Journal of Case Reports and Images 2014;5(5):365–369. |
|
Abstract
|
|
Introduction:
Splenic cysts are uncommon findings whose treatment is usually surgical if more than five centimeters.
Case Report: A case of a self resolving symptomatic large non parasitic splenic cyst is reported. Conclusion: Even if general guidelines prescribe a surgical treatment for >5 cm splenic cyst, sometimes a wait-and-see strategy could be adopted, with the consent of the patient and keeping an eye on his/her general conditions. | |
|
Keywords:
Spleen, Splenic cyst, Splenectomy, Non-surgical treatment
| |
|
Introduction
| ||||||
|
Splenic cysts are uncommon findings. Their treatment is usually based on their size and probable etiology. Open or laparoscopic splenectomy remains the treatment of choice in particular for large cysts, even if less invasive procedures, such as partial splenectomy, marsupialization or simple drainage, are gaining popularity as they allow maintaining splenic function. Conservative non-surgical treatment has been proposed for cysts whose size is less than 4 cm, whereas larger lesions would require an operative approach to avoid complications such as rupture or infection, as they are supposed to be unlikely to regress spontaneously. Herein, we report a case of a big splenic cyst that resolved without any treatment but observation. Current policies and indications for surgery in case of splenic cyst should be revised. | ||||||
|
Case Report
| ||||||
|
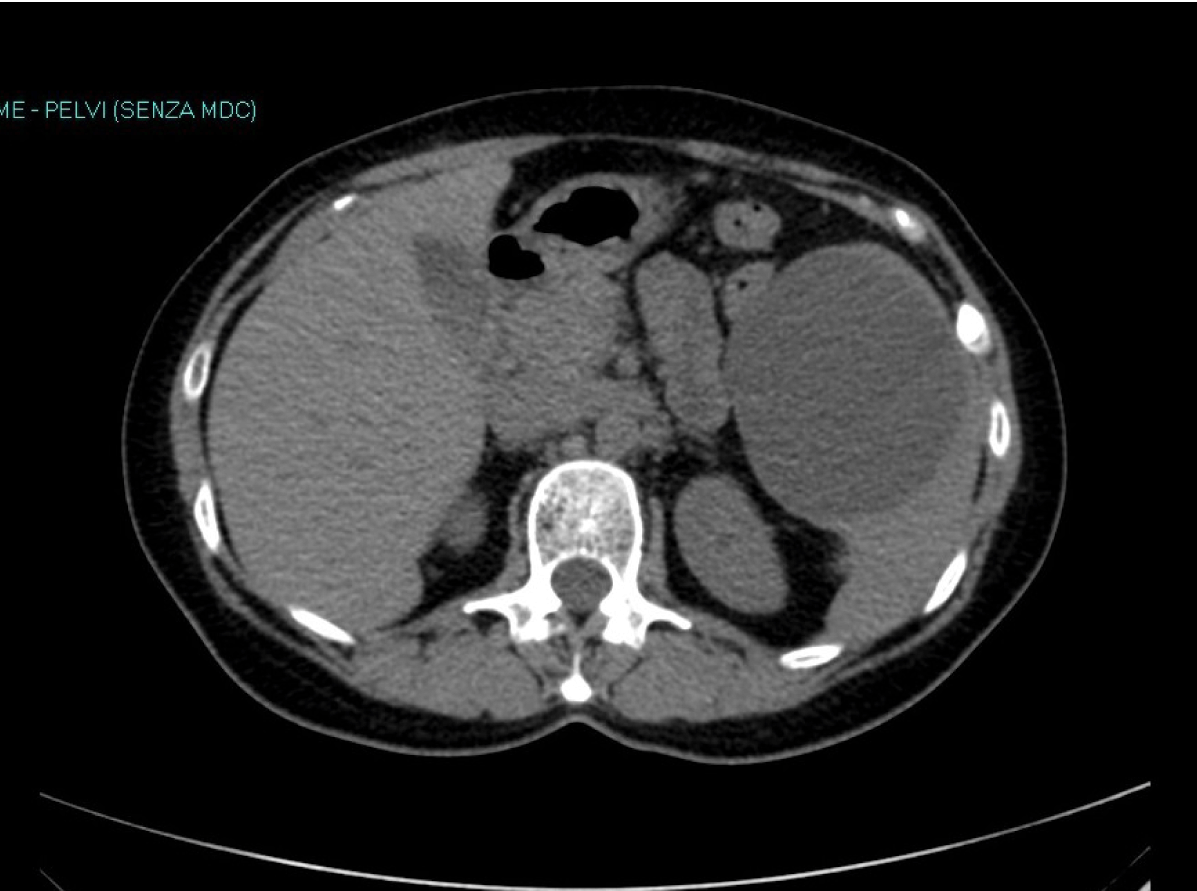
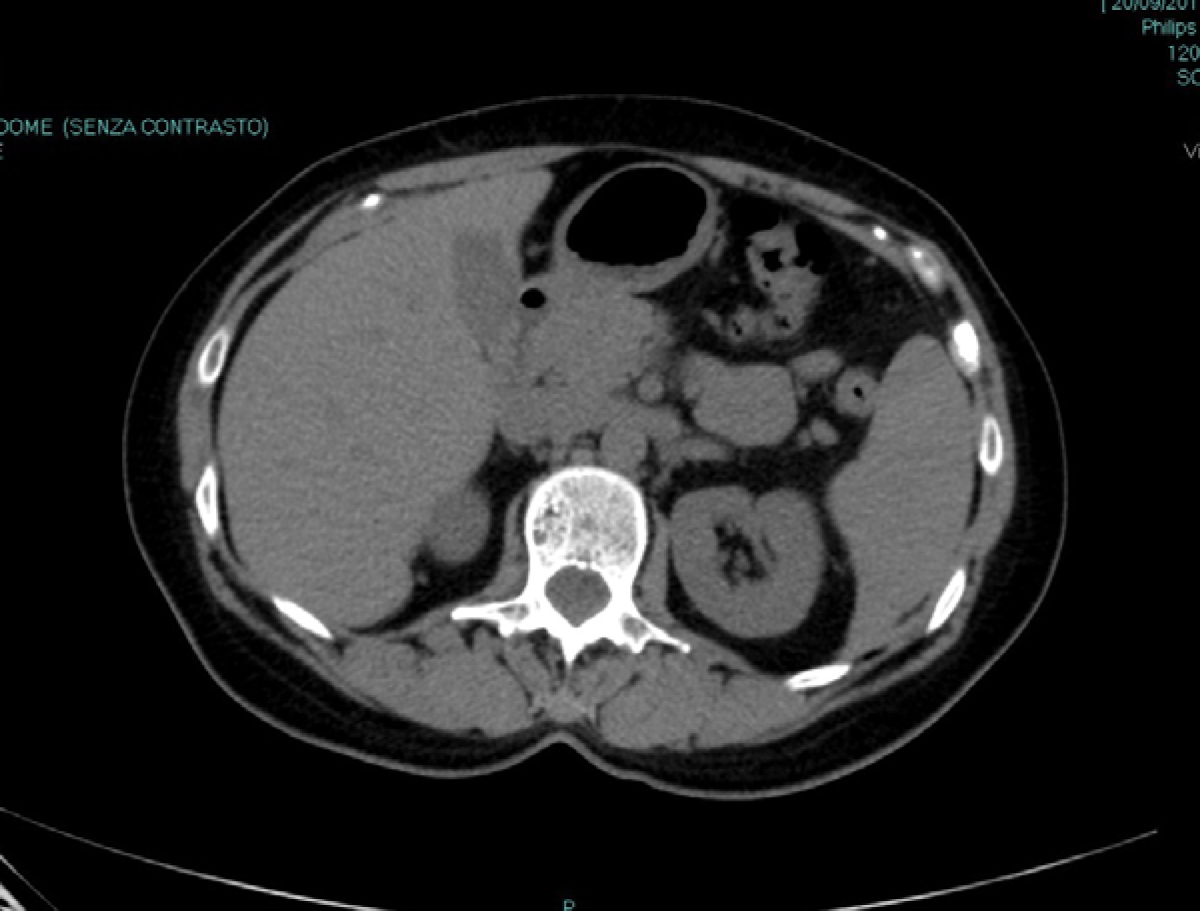
A 42-year-old female (anesthetist by profession) presented with sudden onset of upper left abdominal pain, left loin pain and left lower chest pain, without any history of trauma, even minimal. She did not complain of any urinary or bowel symptom and had never seen blood in her urine or stools. She had no angina-like pain or any breathing problem. Her past medical history was completely unremarkable and she had not had any trip abroad in the last five years. General conditions were good and vitals were normal. Physical examination revealed an area of tenderness at the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, without any guarding or rebound, where a deep mass could be palpated. Urine test and culture were negative. Blood test showed no abnormality, in particular no anemia or eosinophilia. Serologic tests for parasites were negative. Ultrasound scan revealed an 8-cm cystic mass of the spleen but no free fluid. Computed tomography (CT) scan (Figure 1) confirmed the presence of an 8-cm cyst of the medial aspect of the spleen without any other relevant abdominal finding. The cyst was apparently simple and thin-walled, without any internal sept or vegetation. The CT scan was unenhanced as patient declined contrast. Following the guidelines, we proposed a laparoscopic total or partial splenectomy, depending on the intraoperative findings, to avoid complication as rupture or infection. After an in-depth discussion with the patient, she was adamant that she would like to avoid any surgery, even laparoscopic. For this reason we agreed to adopt a wait-and-see strategy. She was monitored for 24 hours in the surgical ward, than discharged. Pain subsided gradually in a week or so. Three months later, a repeat CT scan (Figure 2) revealed that the cyst had completely disappeared. Now, more than 2 years after that episode of pain, the patient is completely fine and asymptomatic. A recent ultrasound scan confirmed the absence of any splenic cyst. | ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
|
Discussion
| ||||||
|
Splenic cysts are generally uncommon findings which tend to present with a variety of nonspecific symptoms such as abdominal fullness, generalized pain, shortness of breath and back pain. [1] [2] [3] Incidence in Europe recently went up to 1% due to the widespread use of ultrasound, [4] but due to the nature of symptoms, a great deal of splenic cysts are chance findings on ultrasound, abdominal CT or even on autopsy. A study carried out by Robbins et al. and published in 1978, revealed 32 benign splenic cysts found incidentally at autopsy in a total of 42,327 patients' autopsy records. [5] While hepatic cysts are mostly congenital or parasitic and rarely malignant or infective and renal cysts are mostly congenital or occasionally related to systemic diseases, splenic cysts are categorized into two groups based on the absence or presence of an epithelial wall. Primary cysts, also known as 'true cysts', have a complete epithelial wall and secondary cysts, or 'false cysts', have an incomplete or no epithelial lining. [1] True cysts are further divided into parasitic or non-parasitic cysts, Parasitic cysts are rare and usually caused by the Echinococcal infection [6] while non-parasitic cysts can then categorized into congenital or neoplastic cysts. Non-parasitic cysts can be true or false. Congenital cysts can be either epidermoid, dermoid or endodermoid cysts, with endodermoid cysts having the highest prevalence of all nonparasitic true cysts at 90%. [7] Neoplastic cysts can be hemangiomas or lymphangiomas. These tend to be multilocular and so, can be diagnosed easily. False cysts comprise about 50–80% of non-parasitic cysts [8] and tend to be post-traumatic as a result of blunt injury to the abdomen, or in some rare cases, are caused by mononucleosis, tuberculosis or malaria. [9] Evenif they are usually asymptomatic and discovered during routine abdominal imaging, they can present with left upper quadrant pain, which can have a sudden onset as in the reported case. More often, when symptomatic, they can give vague abdominal pain due to capsular distension or pressure on the surrounding structures. [10] Ultrasound scan and CT scan are the procedures of choice to investigate the cyst and the bases of the choice of the treatment. Blood tests can be useful in discriminating a parasitic etiology. The management of splenic cysts depends on the type of pathogenesis involved, the size and any possible complications, and while there is still controversy surrounding the optimal management of these cysts, surgery is evidently the first port of call. Research recommends some form of surgical intervention for cysts which are symptomatic or complicated, or greater than 4–6 cm in diameter. [11] [12] This is especially true for post-traumatic cysts, which should be managed when the diameter exceeds 4 cm due to the greater risk of rupture and infection such as hemoperitoneum, abscess formation and chemical peritonitis. [9] [13] Both open and laparoscopic techniques can be used, however, preference is given to laparoscopic methods as they are minimally invasive, with shorter hospitalization time and lower rates of post operative pain. [2] Cysts which are less than 5 cm in diameter should be managed conservatively with regular scans and surgery only being considered if necessary to alleviate symptoms. [9] There are a variety of surgical methods involved in splenic cyst treatment and factors influencing the surgical procedure selected are: patient age, size and location of cyst, and type of cyst. [3] These include percutaneous drainage, total splenectomy, partial splenectomy, marsupialization and fenestration. [9] Percutaneous drainage is now considered an effective way of reducing the size of large cysts pre-operatively before a more effective surgical method is used to prevent recurrence. [14] Total and partial splenectomy can both be performed laparoscopically with partial splenectomy being preferred as splenic parenchyma is preserved enabling regular immunological function of the spleen if enough is saved. [9] [15] Marsupialization is a method of separating the splenic tissue from the cyst [9] and due to the low recurrence rate experienced, it is recommended in the management of superficial cysts. [16] Finally, fenestration methods involve resecting only a segment of the cyst wall. This allows for communication between the peritoneal cavity and cyst cavity but has been reported to have a high recurrence rate, irrespective of whether laparoscopic or open methods are used. [13] It is important to acknowledge that every operative approach has a potential for complications, such as pancreatic injury with pancreatitis or fistula, stomach or bowel injury, diaphragmatic injury with or without pneumothorax and loss of splenic function with the risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy sepsis. [17] This case report, however, illustrates the possibility of spontaneous regression of cysts with no surgical intervention being necessary. While a conservative approach was an unusual strategy to adopt, with a multitude of surgical options being available, it was carried out at the request of the patient. A similar case was reported in 2009 involving a female patient who initially presented with a 6-cm true cyst, which regressed to a 1.8x1.4 cm cystic lesion in nine years. [1] While, in general, the first choice of management in non- parasitic splenic cysts should be laparoscopic surgery which preserves spleen parenchyma, it is important to consider the possibility of spontaneous cyst regression. [18] This can occur following parenchymal rearrangement and tissue scarring enabled by the absence of a true epithelial lining. The patient should be informed and given the two possible options, surgery or wait-and-see, in particular in the absence of hemodynamic abnormalities and when the CT scan shows a clear diagnosis of non-parasitic cyst and excludes a malignant etiology. In this regard, an enhanced CT scan is the best diagnostic tool, should the patient agree to receive intravenous contrast. | ||||||
|
Conclusion
| ||||||
|
Self resolution of splenic cysts is not a heavily documented phenomenon as most cases are resolved early on with surgery, but should be a consideration especially in uncomplicated cysts. Regular follow-up and computed tomography scans would enable cyst progression to be tracked and if patients remain asymptomatic, it would eliminate the need for surgery and all associated risks. | ||||||
|
References
| ||||||
| ||||||
|
[HTML Abstract]
[PDF Full Text]
|
|
Author Contributions
Meetal Shah – Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting the article, Final approval of the version to be published Abdul Quyyum Khan – Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Drafting the article, Final approval of the version to be published Maria Vittoria Cavalletti – Conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and interpretation of data, Critical revision of the article, Final approval of the version to be published Luciano Perrone – Acquisition of data, Critical revision of the article, Final approval of the version to be published Chenji Ratnavel – Analysis and interpretation of data, Critical revision of the article, Final approval of the version to be published Giovanni Domenico Tebala – Conception and design, Analysis and interpretation of data, Critical revision of the article, Final approval of the version to be published |
|
Guarantor of submission
The corresponding author is the guarantor of submission. |
|
Source of support
None |
|
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest. |
|
Copyright
© 2014 Meetal Shah et al. This article is distributed under the terms of Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium provided the original author(s) and original publisher are properly credited. Please see the copyright policy on the journal website for more information. |
|
|
|
About The Authors
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||